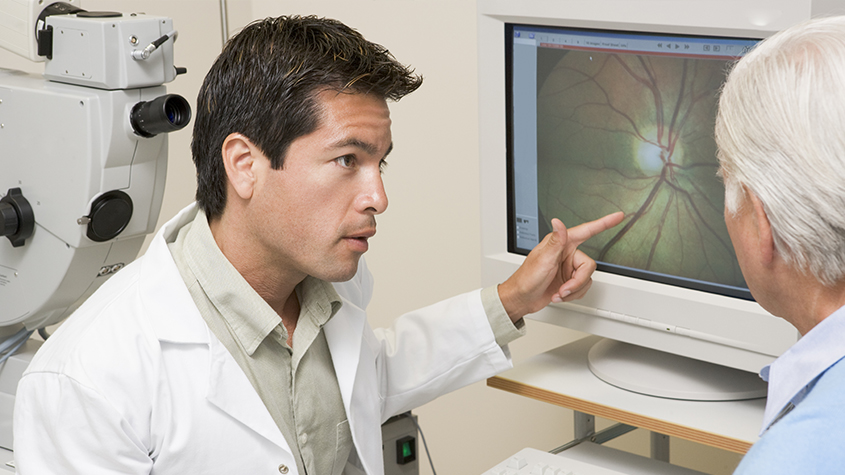
Both optometrists and ophthalmologists treat many common types of ocular disease. However, for the best outcome, it’s important to see an eye doctor regularly. They can identify any issues before they become serious problems.
Fortunately, they can treat all of the diseases mentioned below, and in some cases, you can do certain things to prevent them from developing. Look at the most recent statistics, and you’ll see why good eye health care matters.
Currently, more than 4.2 million people in the U.S. alone over the age of 40 are partially blind or have poor visual acuity. Although a lot of things cause these problems, the ocular diseases listed below are the most common.
Macular Degeneration
This is commonly referred to as “age-related macular degeneration” because it affects seniors. Not only does it cause blurriness and distortion but left untreated, individuals lose their central vision. In other words, they are unable to see anything through the center portion of the eye.
Two types of this ocular disease exist. First, wet macular degeneration means that abnormal blood vessels that are located behind the retina grow under the macular. Along with leaking blood and fluid, this leads to scarring and, sometimes, permanent damage. Second, dry macular degeneration progresses slowly as part of the natural aging process. Typically, it affects both eyes at some point.
Cataracts
Roughly 20 million people in the U.S. over the age of 40 have cataracts in either one or both eyes. While they can develop in children, teens, and young adults, cataracts are most often associated with age. With this, a film covers the eye, which, in turn, makes everything appear blurry.
Of all the different kinds of ocular diseases that lead to blindness worldwide, cataracts rank number two. Fortunately, an eye doctor can remove the damaged lens, followed by implanting an artificial one. After recovery, patients see amazingly well.
Diabetic Retinopathy
If you have diabetes, then you’re at risk of developing this ocular disease. This particular disease causes progressive damage to the retina’s blood vessels. The first stage consists of mild non-proliferative retinopathy and then moderate non-proliferative retinopathy, which blocks some of the vessels.
Then, it moves into stage three or severe non-proliferative retinopathy, which means more blood vessels become blocked. The fourth and final state, proliferative retinopathy, is the most advanced. Although Diabetic Retinopathy does affect just one eye on occasion, it typically involves both eyes.
Start by improving your overall health. Eat balanced meals, keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels down, and take insulin. In addition, regular exercise, losing weight, and giving up smoking all make a huge difference. From there, a qualified eye doctor can provide you with treatment options to reduce the risk of losing your vision.
Glaucoma
Many people think glaucoma is one type of ocular disease. However, it’s a group of diseases that cause damage to the optic nerve. When that happens, people face the risk of losing their sight completely. With glaucoma, the fluid pressure inside the eyes gradually rises.
There are also two categories of glaucoma: open-angle and closed-angle. Not only is open-angle glaucoma chronic, but it also progresses slowly. Often, a person can have this type without knowing it. Unfortunately, they don’t realize there’s an issue until they have a comprehensive eye exam performed.
As for closed-angle glaucoma, it’s usually painful and it comes on suddenly. In addition, an individual can lose their vision much faster with this kind of glaucoma compared to the open-angle kind. Because this happens fast and involves pain, it’s diagnosed much quicker as well.
For these common types of ocular diseases, it’s important to have your vision checked. If an ocular disease is diagnosed, your optometrist will be able to determine the best treatment plan for optimal eye health and vision.
Read More